Loose Design For Web Apps
Disclosure: "This article is personal opinion of research based on my experience of almost 20 years. There is no third party advertising on this page or monetised links of any sort. External links to third party sites are moderated by me. Disclaimer. " Shaun Anderson, Hobo

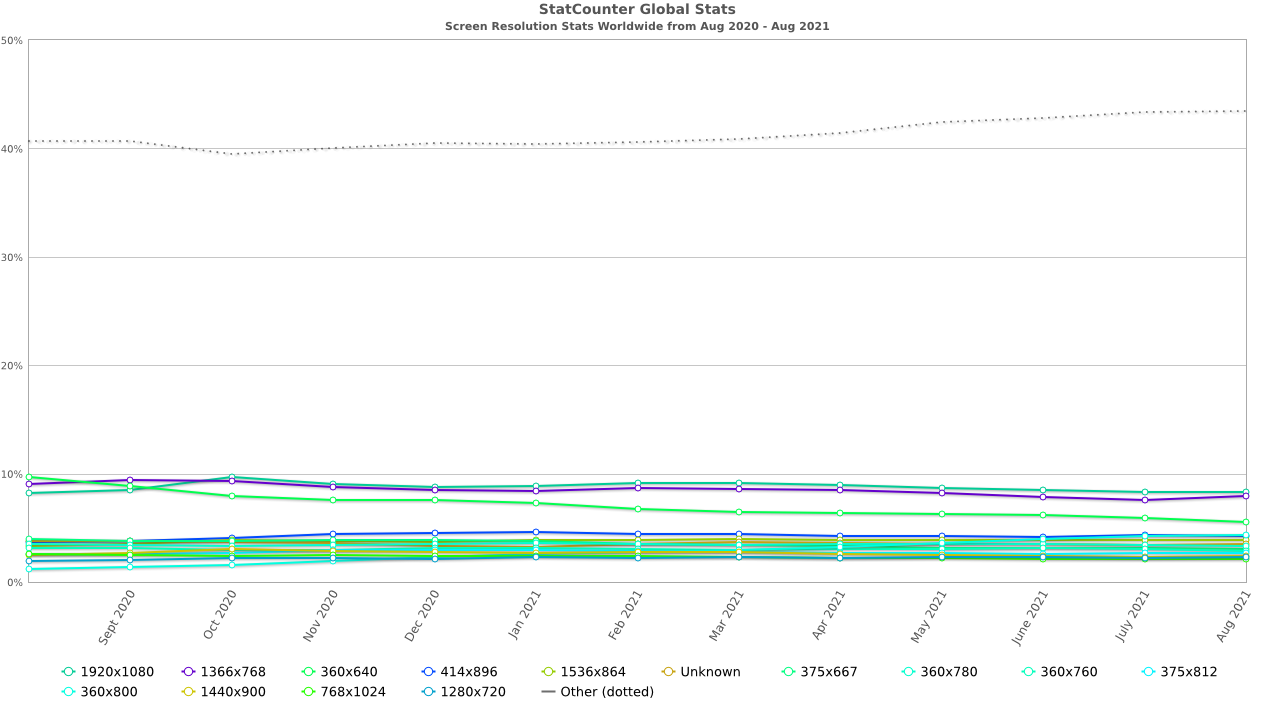
There's no one best screen size to design for. Websites should transform responsively and fast at all screen resolutions on different browsers and platforms. Accessible. Mobile-friendly. Design for your audience, first. Design from 360×640 through 1920×1080.
Also:
- Design for desktop displays from 1024×768 through 1920×1080
- Design for mobile displays from 360×640 through 414×896
- Design for tablet displays from 601×962 through 1280×800
- Check Google Analytics and optimise for your target audience's most common resolution sizes
- Do not design for one monitor size or screen resolution. Screen sizes and browser window state vary among visitors.
- Design should be responsive and fast. Use a liquid or responsive layout that transforms to the current user's window size.
- Monitor Google Search Console mobile-friendly and usability alerts
It should still look good and work well at all sizes, which is why I *used to* recommend a highly accessible liquid layout using percentage widths to control layout. Now the recommendation is a responsive website template.
The three main criteria for optimising a page layout for a certain screen size are:
- Web Page Initial visibility: Is all key information visible above the fold so users can see it without scrolling? This is a tradeoff between how many items are shown vs. how much detail is displayed for each item.
- Web Page Readability: How easy is it to read the text in various columns, given their allocated width?
- Web Page Aesthetics: How good does your page look when the elements are at the proper size and location for this screen size? Do all the elements line up correctly — that is, are captions immediately next to the photos, etc.?
Usability guidelines also recommended you consider all three criteria at the full range of sizes,. Check the browser window from 360×640 to 1920×1080 screen resolutions.
Your page should score high on all criteria throughout the entire resolution range.
Your page should also work at even smaller and bigger sizes, though such extremes are less important.
Although such users should certainly be able to access your site, giving them a less-than-great design is sometimes an acceptable compromise.
Top Ten Most Common Screen Resolutions
Visitor analysis of almost half a million visitors in the last year:
| 1 | 1920×1080 | 104,190(22.62%) |
| 2 | 1366×768 | 51,580(11.20%) |
| 3 | 1440×900 | 44,003(9.55%) |
| 4 | 1536×864 | 39,606(8.60%) |
| 5 | 2560×1440 | 34,152(7.41%) |
| 6 | 1680×1050 | 19,730(4.28%) |
| 7 | 1280×720 | 16,364(3.55%) |
| 8 | 1280×800 | 10,719(2.33%) |
| 9 | 1792×1120 | 9,494(2.06%) |
| 10 | 1600×900 | 8,630(1.87%) |
A Responsive Website Template Is MUST
QUOTE: "Google recommends Responsive Web Design because it's the easiest design pattern to implement and maintain" Google Developer Guides, 2021
In today's world, a lot of people are using handheld devices (tablets and smartphones) to browse the web and responsive website design (RWD) has emerged as a very likely solution (it is still debated by aficionados) to screen size challenges.
This method moves away from using fixed-width websites and instead uses Media Queries in CSS style sheets to create a website that responds in size to the different viewports of handheld devices and smaller screens that people use.
So whatever device a person may be using to view your website you are able to give them the fullest experience possible.
Sign up for our Free SEO training course to find out more.
Table of Contents
Google Prefers Mobile-Friendly Sites
Google dictates the ebb and flow of online commerce and they've just dictatedyou need to design for a satisfying user experience across multiple devices IF you want to expect to rank high for competitive keywords in Google.
QUOTE : "Google uses two different crawlers for crawling websites: a mobile crawler and a desktop crawler. Each crawler type simulates a user visiting your page with a device of that type. Google uses one crawler type (mobile or desktop) as the primary crawler for your site. All pages on your site that are crawled by Google are crawled using the primary crawler. The primary crawler for all new websites is the mobile crawler. In addition, Google recrawls a few pages on your site with the other crawler type (mobile or desktop). This is called thesecondary crawl, and is done to see how well your site works with the other device type." Google Webmaster Guidelines, 2020
Since April 21, 2015, globally, how mobile-friendly a site has affected ranking performance for websites across a variety of devices.
If you make websites for small businesses – you'll know they want a website that will perform well in Google organic listings – you know they are interested in search engine optimisation:
QUOTE: "I have 20 years of experience practicing professional SEO. This SEO tutorial is my collection of tips and SEO best practices I use to rank websites in Google." Shaun Anderson, Hobo 2020
SEO is now based, in part, on good website UX, as Google quantifies it, at least for mobile users.
QUOTE: "With mobile searches now exceeding desktop searches, it's important that your site be mobile-friendly. Googlebot now uses a mobile crawler as the default crawler for websites." Google Webmaster Guidelines, 2020
At the moment – that essentially now means responsive website design and mobile-friendly, especially with Google "making our index mobile-first ".
Sign up for our Free SEO training course to find out more.
For reference, here is a list of the current top screen resolutions worldwide as recorded recently (2020):
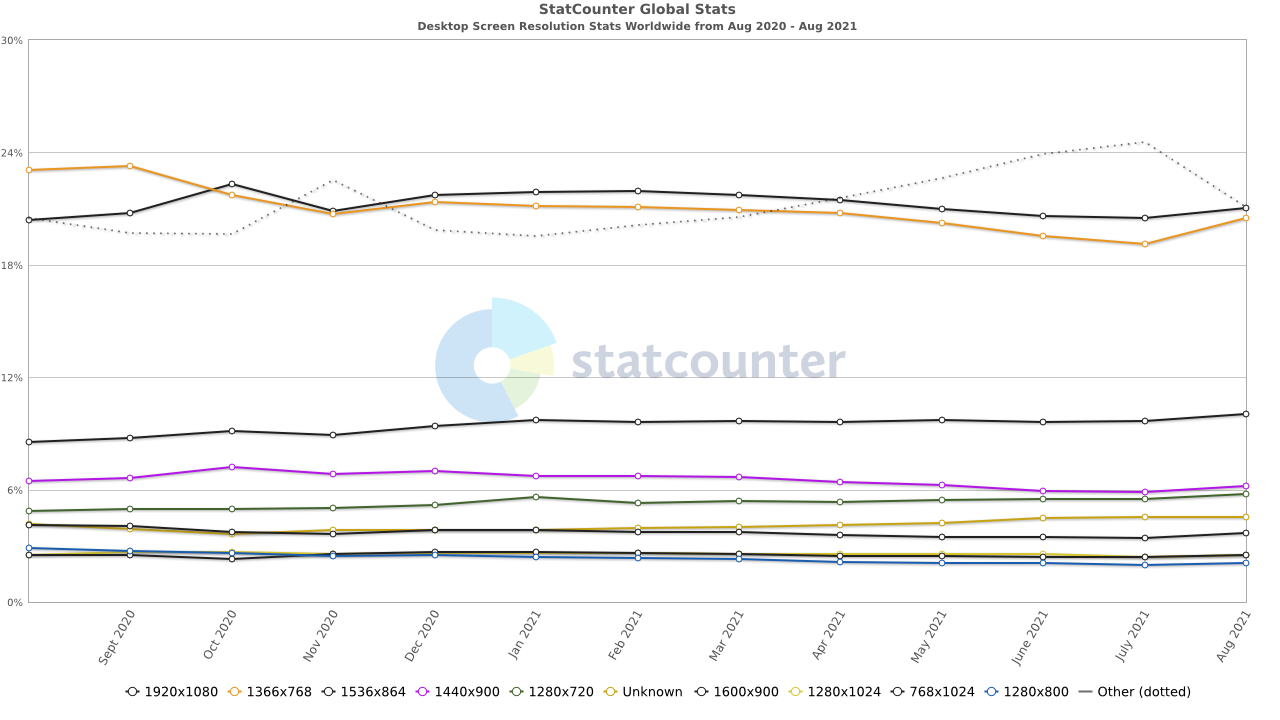
Most Common Desktop Screen Resolution Sizes Worldwide
- 1920×1080 – 21.04%
- 1366×768 – 20.48%
- 1536×864 – 10.05%
- 1440×900 – 6.17%
- 1280×720 – 5.79%
- 1600×900 – 3.68%
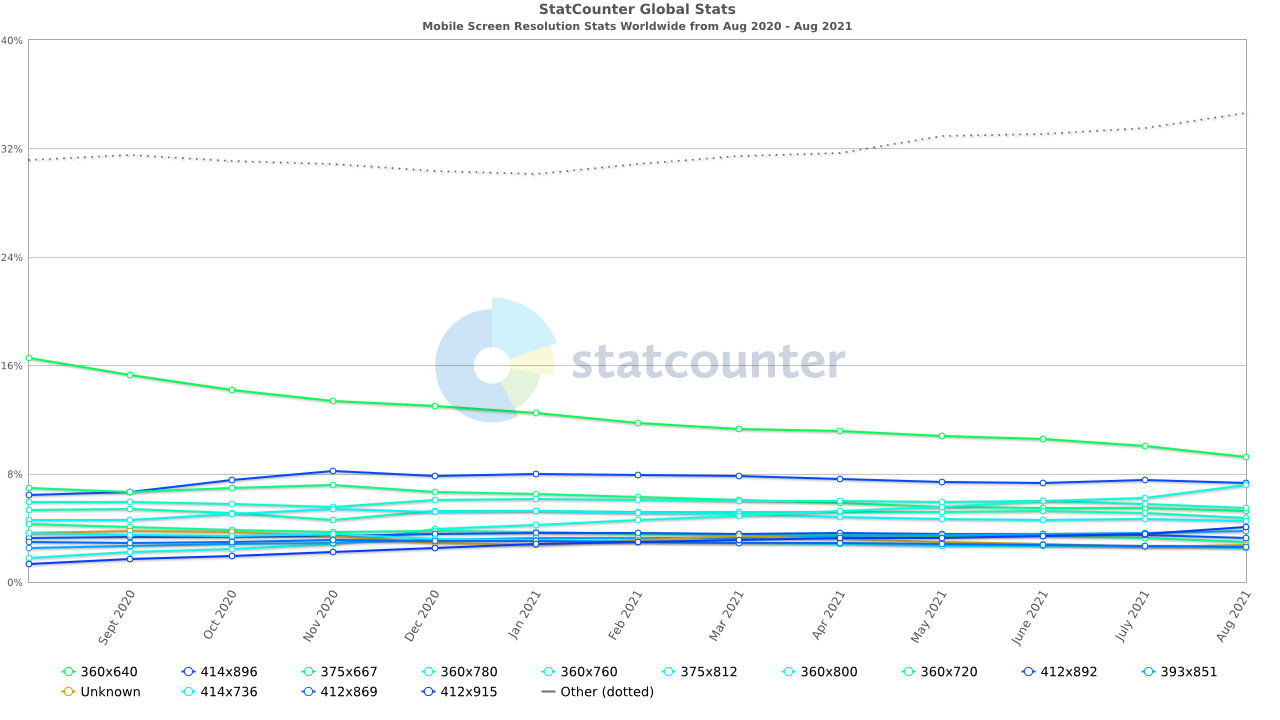
Most Common Mobile Screen Resolution Sizes Worldwide
- 360×640 – 9.25%
- 414×896 – 7.29%
- 360×800 – 7.13%
- 360×780 – 5.43%
- 375×667 – 5.25%
- 360×780 – 4.76%
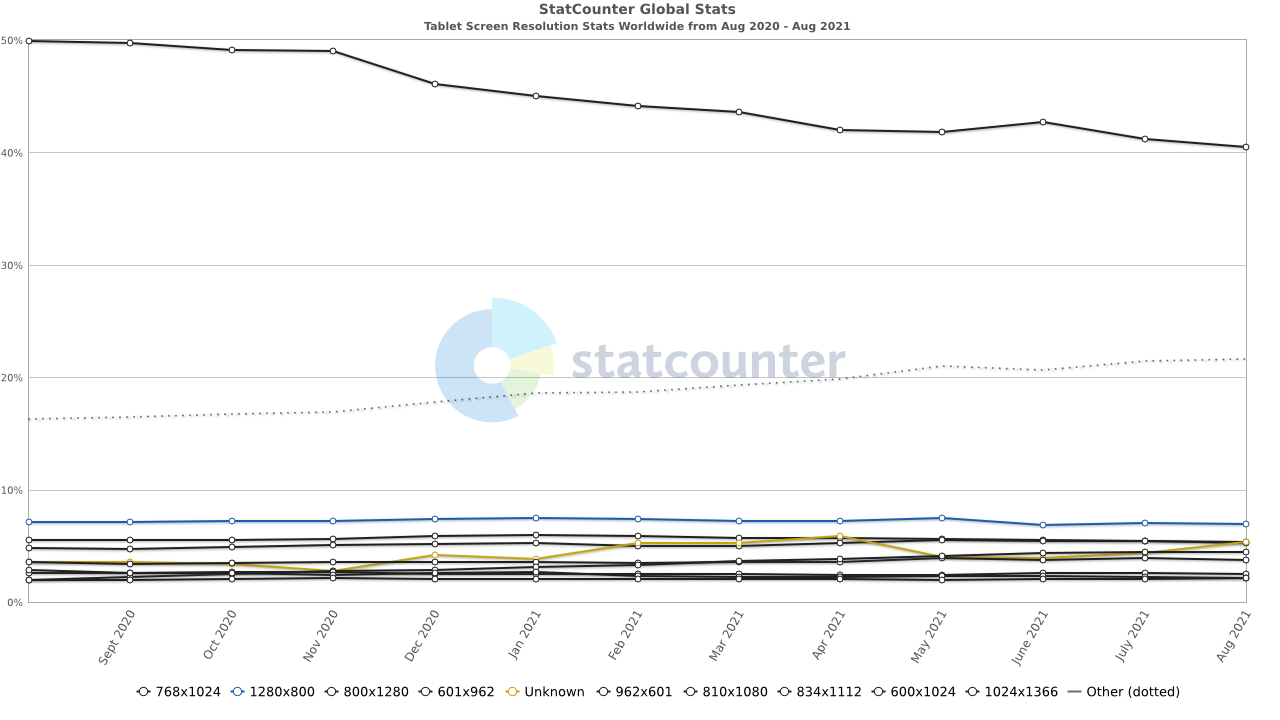
Most Common Tablet Screen Resolution Sizes Worldwide
- 768×1024 – 40.53%
- 1280×800 – 6.91%
- 800×1280 – 5.36%
- 601×962 – 5.21%
- 810×1080 – 4.47%
- 962×601 – 3.79%
Top Screen Resolutions in the US (2021)
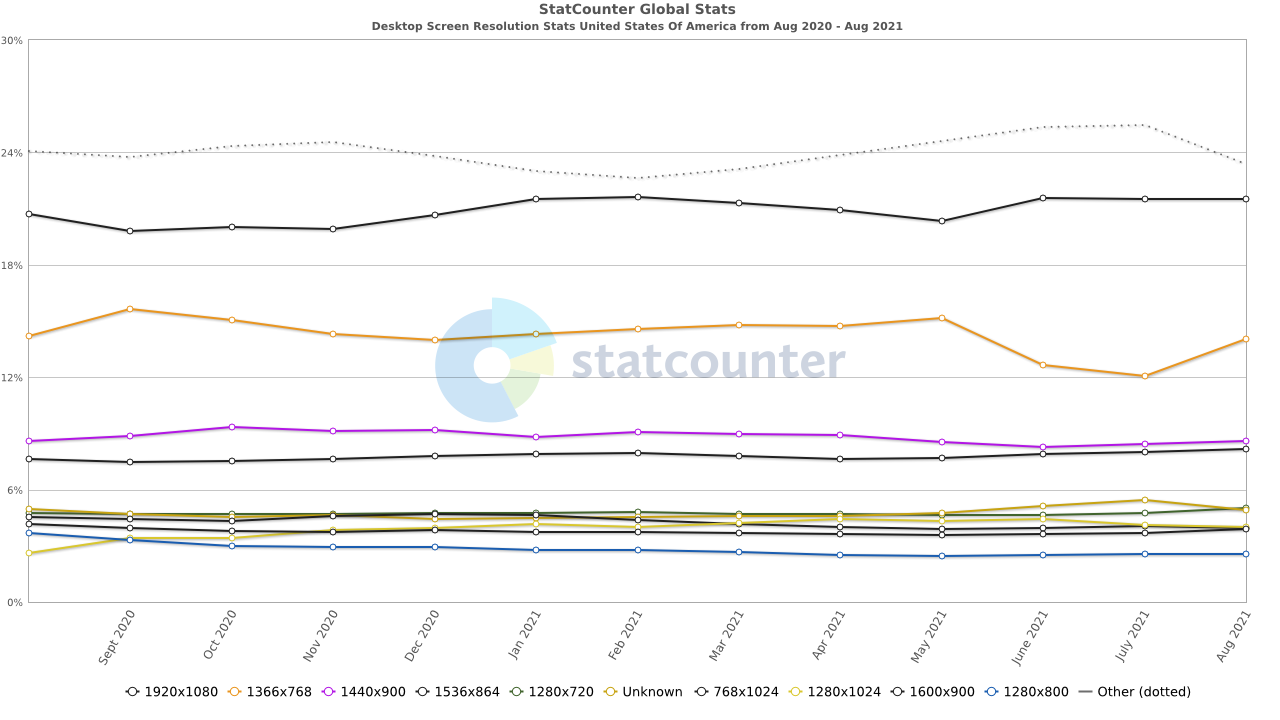
Most Common Desktop Screen Resolution Size in the United States Of America
- 1920×1080 – 21.52%
- 1366×768 – 13.95%
- 1440×900 – 8.58%
- 1536×864 – 8.17%
- 1280×720 – 5.01%
- 1280×1024 – 4.02%
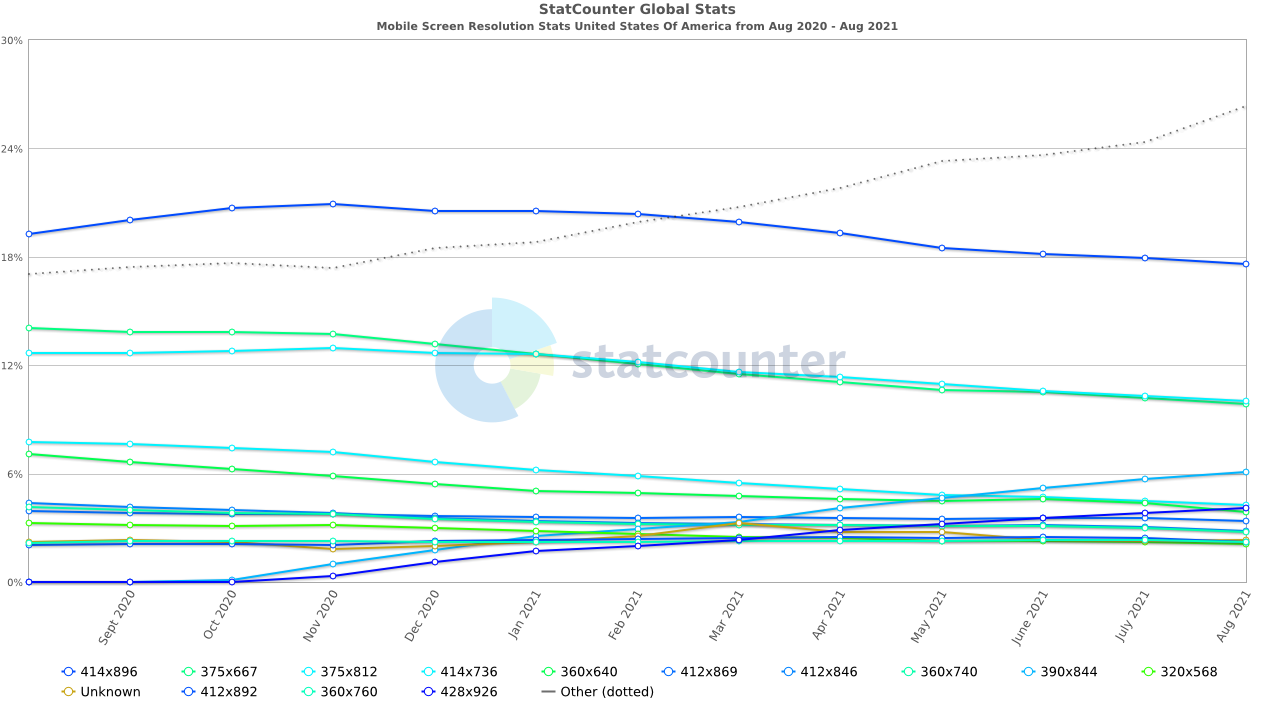
Most Common Mobile Screen Resolution Size in the United States Of America
- 414×816 – 17.62%
- 375×812 – 10.04%
- 375×667 – 9.88%
- 390×844 – 6.1%
- 414×736 – 4.25%
- 428×926 – 4.07%
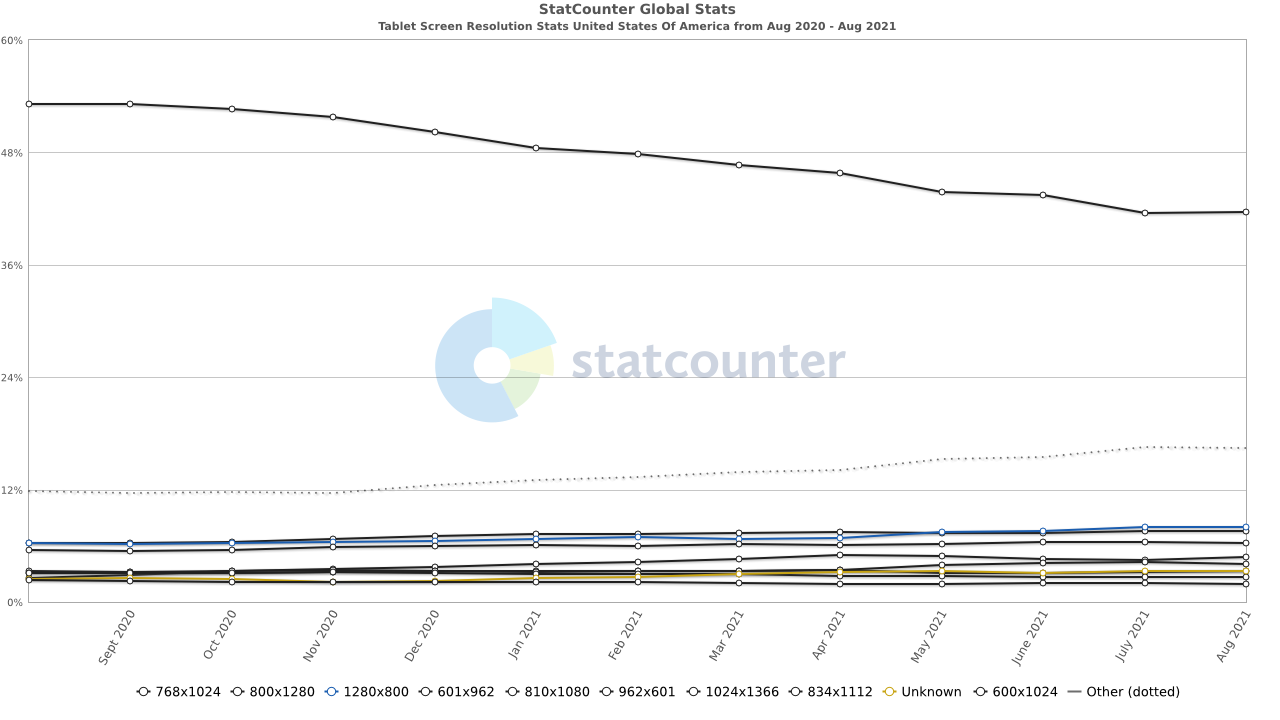
Most common Tablet Screen Resolution Size in the United States Of America
- 768×1024 – 41.63%
- 800×1280 – 7.98%
- 1280×800 – 7.57%
- 601×962 – 6.33%
- 910×1080 – 4.78%
- 962×601 -4.12%
Top Screen Resolutions in the UK (2021)
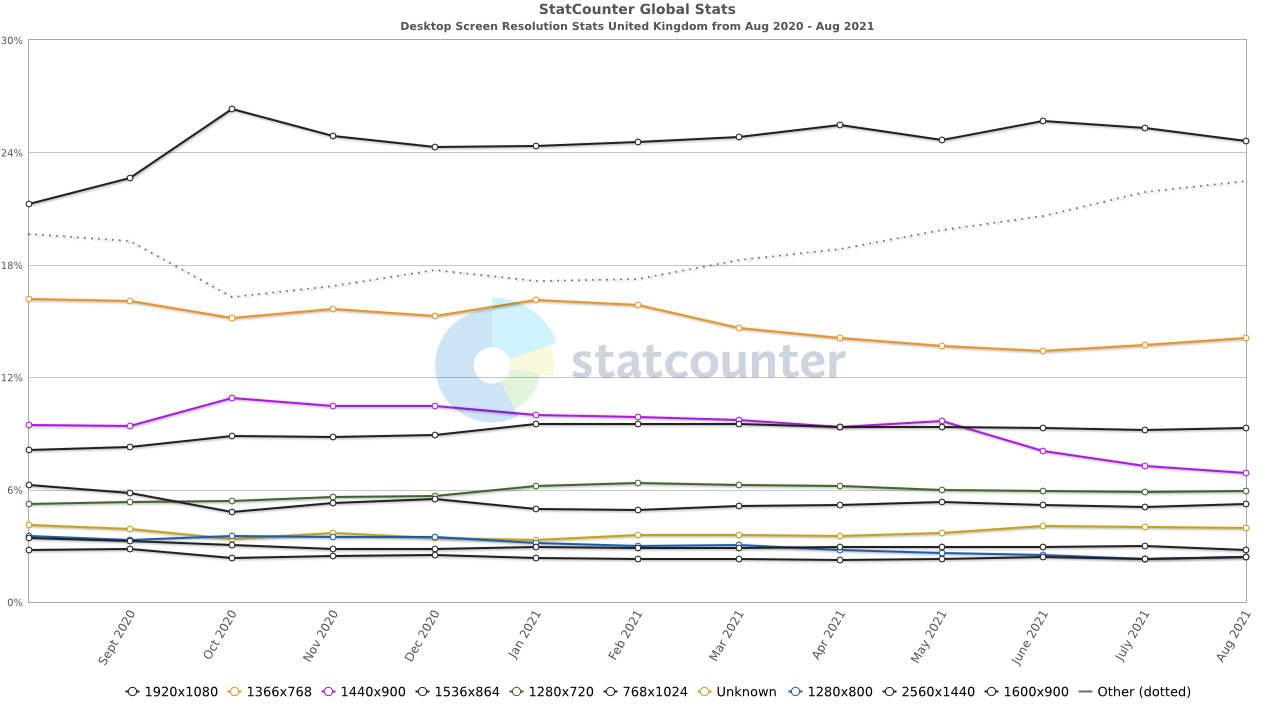
Most Common Desktop Screen Resolution Size in the United Kingdom
- 1920×1080 – 24.53%
- 1366×768 – 14.1%
- 1536×864 – 9.28%
- 1440×900 – 6.87%
- 1280×720 – 5.9%
- 768×1024 – 5.25%
Mobile Screen Resolution Stats in the UK Aug 2020 – Aug 2021

Most Common Mobile Screen Resolution Size in the United Kingdom
- 414×816 – 14.51%
- 375×667 – 12.47%
- 375×812 – 7.21%
- 360×640 – 5.43%
- 412×915 – 5.18%
- 360×780 – 5.04%
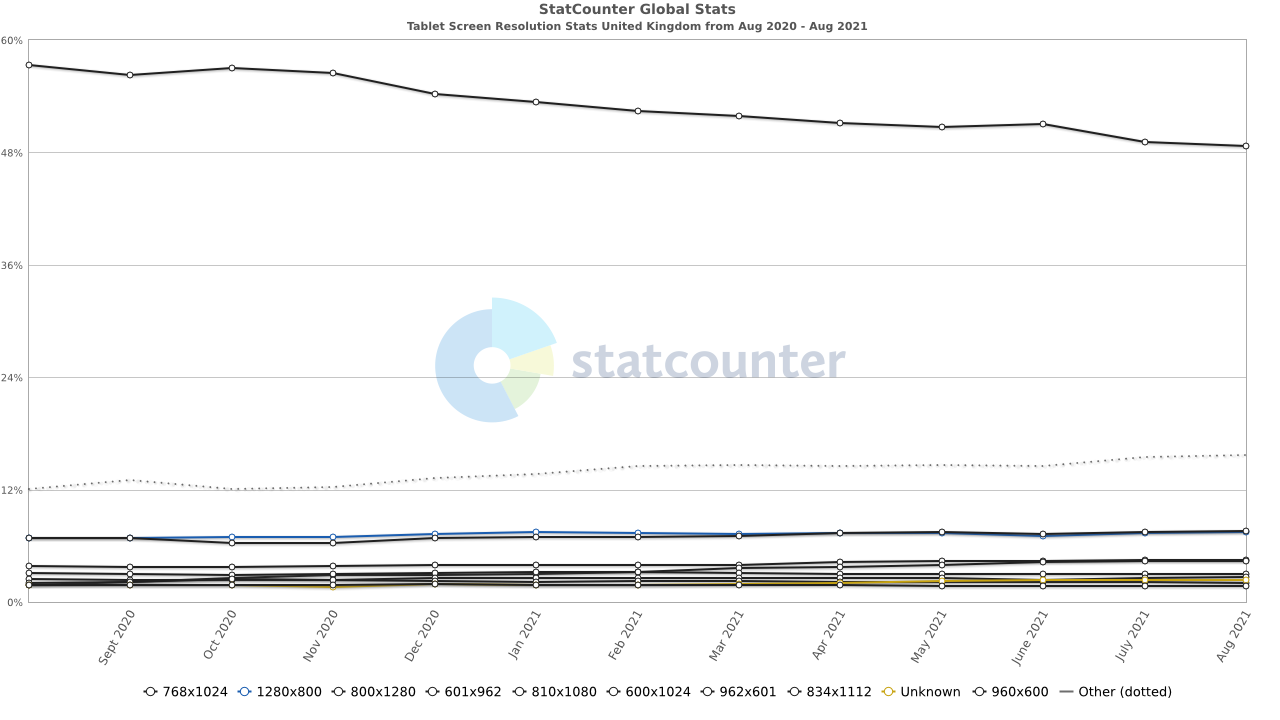
Most Common Tablet Screen Resolution Sizes in the United Kingdom
- 768×1024 – 48.64%
- 1280×800 – 7.55%
- 800×1280 – 7.44%
- 601×962 – 4.5%
- 810×1080 – 4.41%
- 600×1024 – 2.95%
Desktop vs Mobile vs Tablet Market Share Worldwide
Aug 2020 – Aug 2021
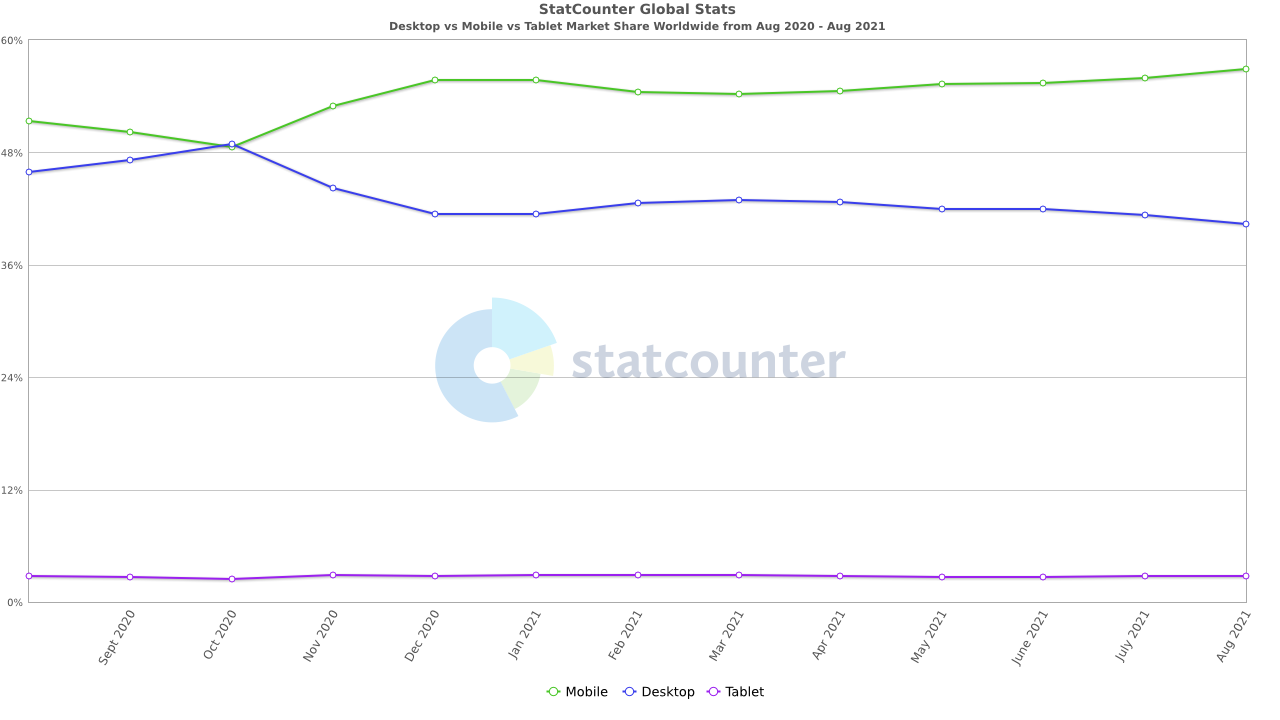
Desktop vs Mobile vs Tablet Market Share Worldwide
- Mobile – 56.94%
- Desktop – 40.3%
- Tablet – 2.76%
*Note – statistics above are from one (albeit credible) source, so could be skewed in ways we might not know.Graphs supplied by http://statcounter.com/.
How Can I Design A Site That Looks The Same In Every Browser & Resolution?
You can't.
It is impossible to design a website to look the same in every browser, platform, and screen resolution, so avoid trying.
You could opt for a fluid layout without tables for your design, with % widths that expand and contract to fit a visitors browser setting OR you could consider looking into responsive design solutions that will achieve much the same thing.
Google favours responsive designs, which is good news for those who have adopted it:
QUOTE: "sites that make use of responsive web design and correctly implement dynamic serving (that include all of the desktop content and markup) generally don't have to do anything." Google NOV 2017
MOBILE IS ON THE RISE – so if developing a new website – you MUST think about how mobile-friendly your website really is from the start.
I aim to keep things simple when I am actually coding things.
You will not – cannot – please everybody – and the questionwhich website size is best is still a hot topic for debate by designers with more usability and UX expertise than I.
What I do know from experience is that it is of critical importance for you to identify YOUR audience and the devices they use, and build your website (on the whole) to suit THAT audience.
And that audience includes GOOGLEBOT.
Sign up for our Free SEO training course to find out more.
Does Your Mobile Site Redirect to Another URL & Version Of Your Site?
Well, that's not ideal. It has never been, in fact.
Way back in the day – some folk used TEXT-ONLY versions of a website to produce content for users/browsers that didn't support elements of their websites – in a (usually vain) attempt to make their content more accessible.
The W3C even used to recommend it I think if all else failed:
A text-only page, with equivalent information or functionality, shall be provided to make a web site comply with the provisions of this part, when compliance cannot be accomplished in any other way. The content of the text-only pages shall be updated whenever the primary page changes. SECTION 508
It's ALWAYS been ideal to deliver one URL to a visitor for accessibility purposes, and there is no difference when delivering mobile or smartphone content if you are thinking about creating "a mobile" version of your site. This, of course, may well be EVEN MORE IMPORTANT if Google is moving to a MOBILE FIRST INDEX.
Google may very well rate you PRIMARILY on your mobile experience in the near future – so we all really need to be aware of the big changes that we might see very soon in Google's SERPs.
When Google is the 'visitor' it's usually even more important to deliver just one URL because of canonical URL challenges for search engines – and this has been the case before the implementation of the canonical link element some time ago.
So the ideal situation is to deliver one URL at all times.
If you have "smartphone" content (which we see as normal web-content, as it's generally a normal HTML page, just tweaked in layout for smaller displays) you can use the rel=canonical to point to your desktop version. This helps us to focus on the desktop version for web-search. When users visit that desktop version with a smartphone, you can redirect them to the mobile version. This works regardless of the URL structure, so you don't need to use subdomains / subdirectories for smartphone-mobile sites.Even better however is to use the same URLs and to show the appropriate version of the content without a redirect John Mueller, Google
Ignoring Google's Recommendations Is Often Not A Smart Move
QUOTE: To recap, currently our crawling, indexing, and ranking systems typically look at the desktop version of a page's content, which may cause issues for mobile searchers when that version is vastly different from the mobile version. Mobile-first indexing means that we'll use the mobile version of the content for indexing and ranking, to better help our – primarily mobile – users find what they're looking for. Webmasters will see significantly increased crawling by Smartphone Googlebot, and the snippets in the results, as well as the content on the Google cache pages, will be from the mobile version of the pages. Google Nov 2017
Google offers the following tips to check your site is prepared for the mobile first index, but essentially, if you are using a responsive web design template for your site you should have minimal issues with this change:
-
Make sure the mobile version of the site also has the important, high-quality content. This includes text, images (with alt-attributes), and videos – in the usual crawlable and indexable formats.
-
Structured data is important for indexing and search features that users love: it should be both on the mobile and desktop version of the site. Ensure URLs within the structured data are updated to the mobile version on the mobile pages.
-
Metadata should be present on both versions of the site. It provides hints about the content on a page for indexing and serving. For example, make sure that titles and meta descriptions are equivalent across both versions of all pages on the site.
-
No changes are necessary for interlinking with separate mobile URLs (m.-dot sites). For sites using separate mobile URLs, keep the existing link rel=canonical and link rel=alternate elements between these versions.
-
Check hreflang links on separate mobile URLs. When using link rel=hreflang elements for internationalization, link between mobile and desktop URLs separately. Your mobile URLs' hreflang should point to the other language/region versions on other mobile URLs, and similarly link desktop with other desktop URLs using hreflang link elements there.
-
Ensure the servers hosting the site have enough capacity to handle potentially increased crawl rate. This doesn't affect sites that use responsive web design and dynamic serving, only sites where the mobile version is on a separate host, such as m.example.com.
Users Expect To Scroll Down A Page
As the first criterion implies, scrolling is always a key consideration. Users generally didn't like to scroll if they do not need to – although, over the years, that's changed.
So, when you design, you should consider how much users can see if they scroll only a screen full or two. Any more than five screens long could be an indication to you that there might be too much copy on the page. Of course, this is balanced with the view that some articles are meant to be in-depth information pieces and users would expect to wait a little longer to view some page content and content types.
Both scrolling and initial visibility obviously depend on screen size: Bigger screens show more content above the fold and require less scrolling.
Will A Change To A Responsive Mobile Site Result In Lots More Traffic From Google?
Not necessarily, but maybe.
As many things to do with Google optimisation – having a mobile-friendly website is more or less to ensure you KEEP the traffic you are already getting, not necessarily give you any more free traffic from Google.
If you don't already get a lot of traffic from mobile visitors – I'm not sure if this update from Google will have a noticeable effect on your traffic levels (in analytics at least) at the outset – but over time – it probably will be an extremely important challenge to navigate.
The quality bar is being raised – again – by Google, and its users – and if you want to compete in ever more competitive organic SERPs this is yet another hurdle for small businesses to get over.
In the LONG term – this mobile conversion can only be a good thing for your users – but in the short term – it will be interesting to see what effect it has on small businesses conversion rates – as conversion rates via mobile are often less than on desktop.
Google has said that this mobile-friendly algorithm will have a greater impact on SERPs than both Google Penguin and Google Panda algorithms – and we'll find out more as time goes on.
How To Check For Important Mobile Usability Issues On Your Site
Google Search Console
You should be able to track mobile errors in GoogleSearch Console (AKA Google Webmaster Tools) and see errors disappear over time if your site is configured correctly.
Sign up for our Free SEO training course to find out more.
Tool To Test Your Site For Mobile Friendliness
- Search Console Url Inspection Tool
- Pagespeed Insights
- Think With Google
- Mobile Friendly Test
How To Make Your Website Mobile Friendly
Part 1 – PageSpeed Insights, Mobile-Friendly Test and Mobile-Usability
Part 2 – Viewports, zoom and plugins
Part 3 – Tap targets, margins and font sizes
Part 4 – Redirects
Web developers should find my other recent post useful now that site speed is a ranking factor in Google:
QUOTE : "The mobile version of a website should ideally load in under 3 seconds and the faster the better. A VERY SLOW SITE can be a NEGATIVE Ranking factor (confirmed by Google). There is no set threshold or speed score to meet, just to make your page as fast as possible." Shaun Anderson, Hobo 2021
Disclaimer
Disclaimer: "Whilst I have made every effort to ensure that the information I have provided is correct, It is not advice.; I cannot accept any responsibility or liability for any errors or omissions. The author does not vouch for third party sites or any third party service. Visit third party sites at your own risk.I am not directly partnered with Google or any other third party. This website uses cookies only for analytics and basic website functions. This article does not constitute legal advice. The author does not accept any liability that might arise form accessing the data presented on this site. Links to internal pages promote my own content and services." Shaun Anderson, Hobo
Loose Design For Web Apps
Source: https://www.hobo-web.co.uk/best-screen-size/
Posted by: schneiderfelist.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Loose Design For Web Apps"
Post a Comment